In modern construction, roof welding is a critical process for ensuring building waterproofing and structural integrity. This article systematically introduces various types of equipment required for roof welding, including their functional characteristics, applicable scenarios, and operational key points, providing comprehensive equipment selection references for engineering teams.
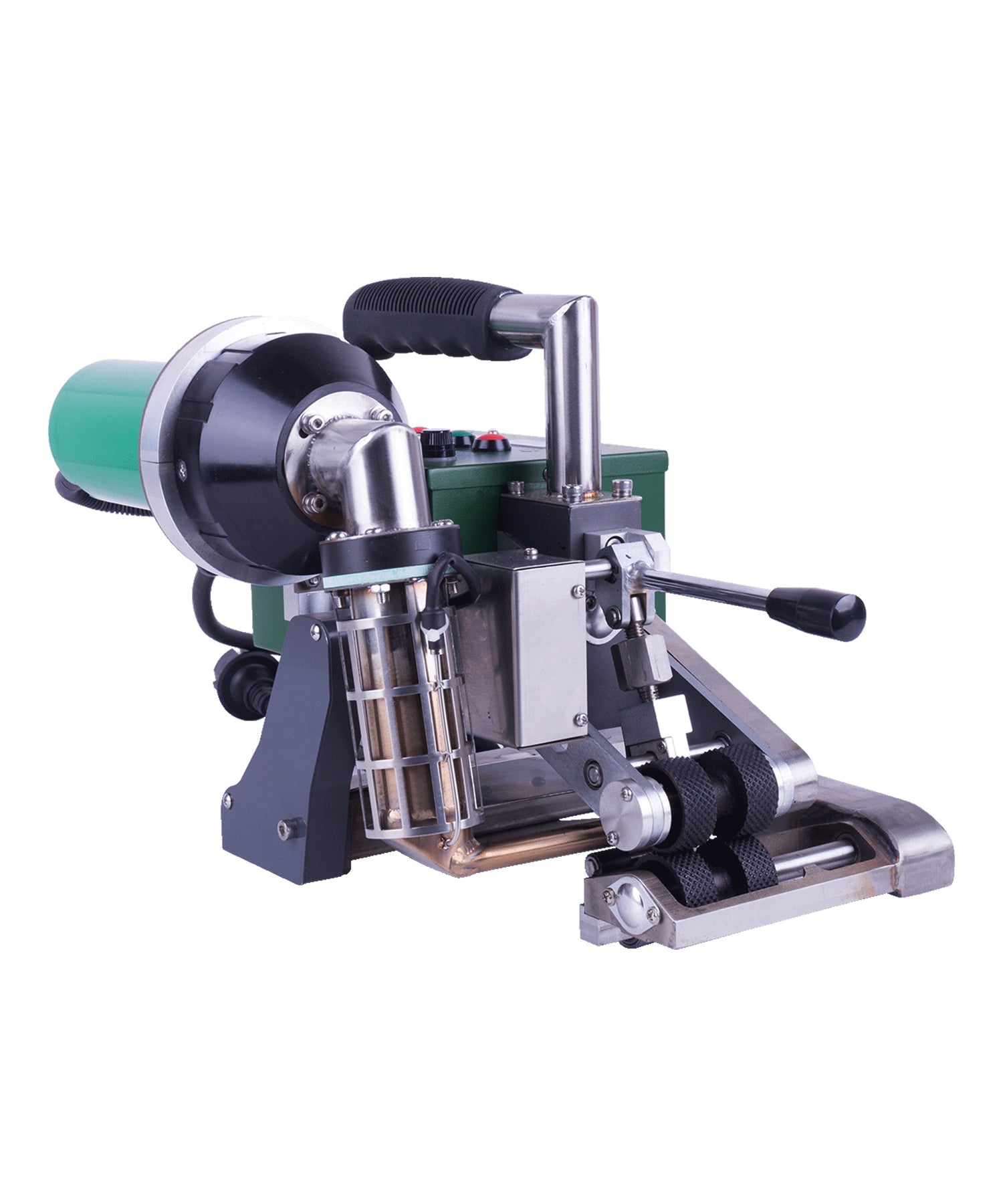
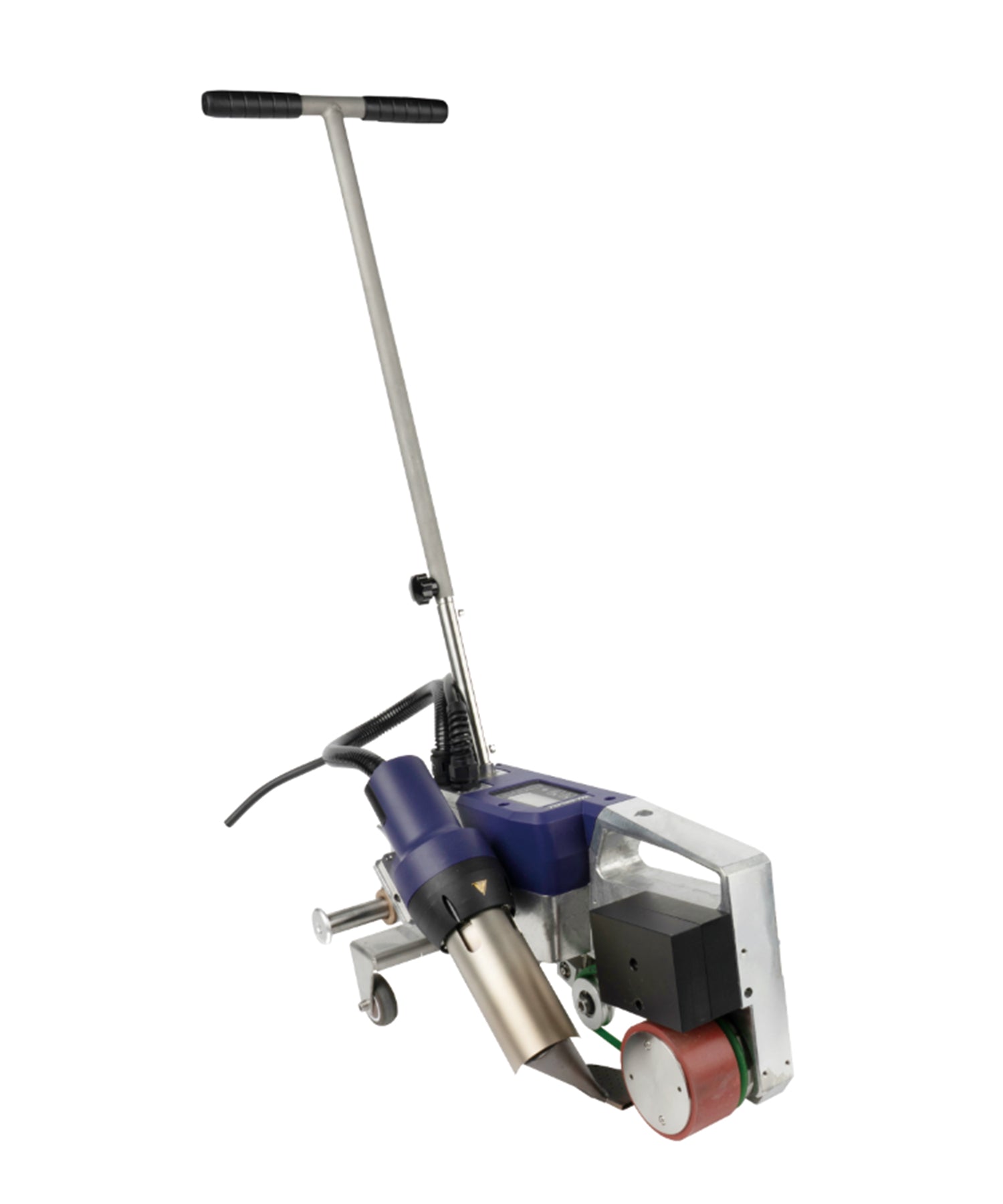
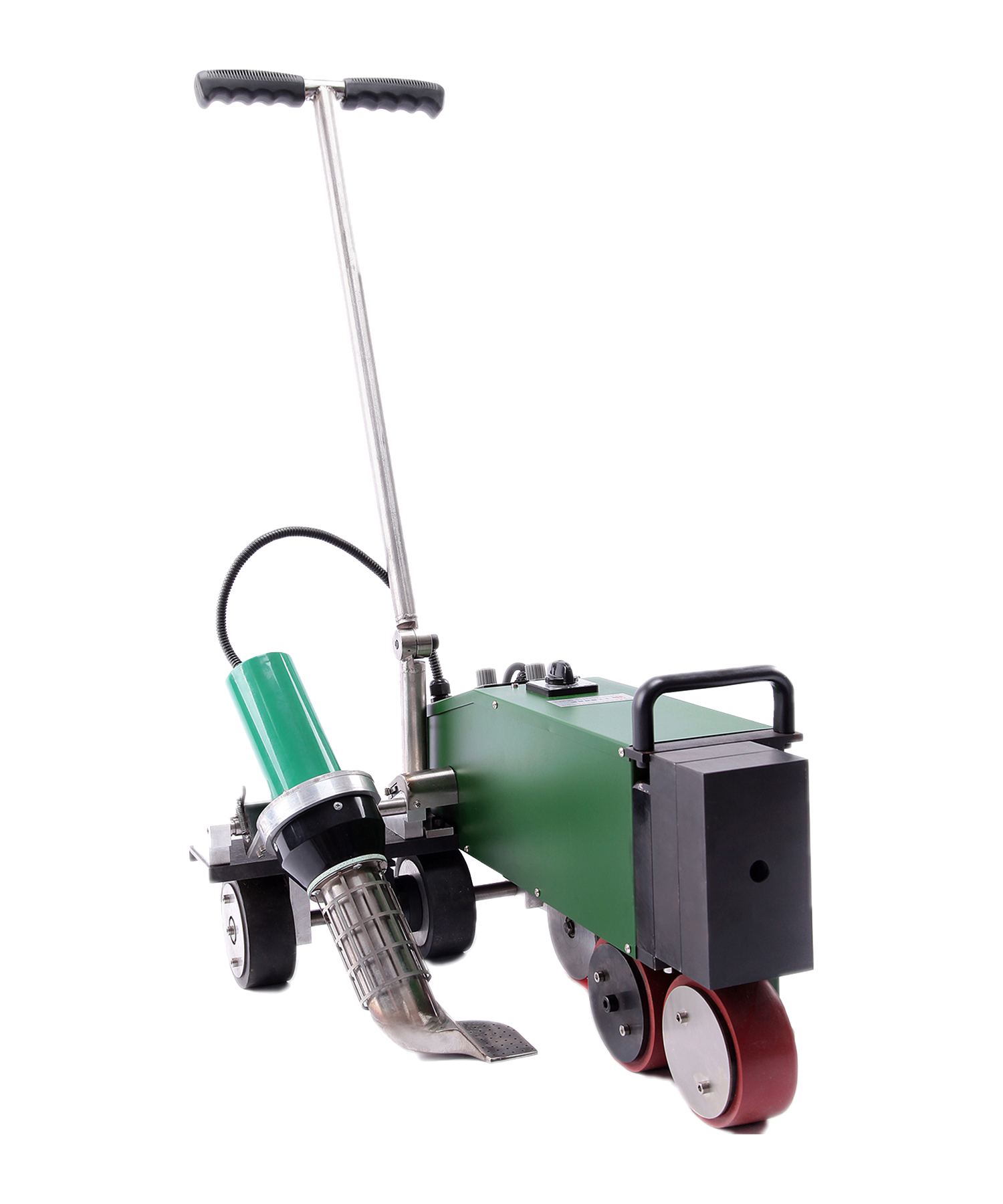
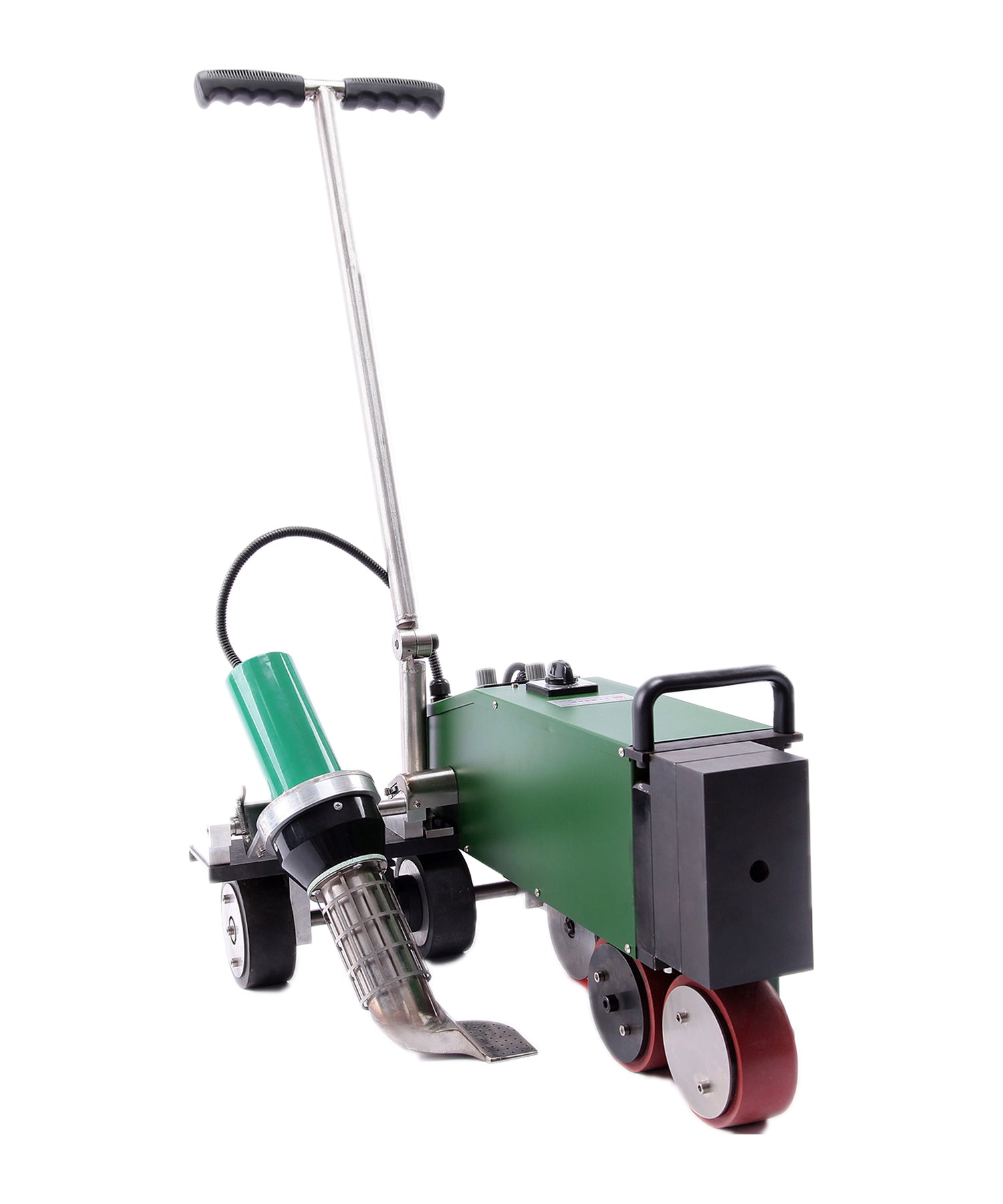
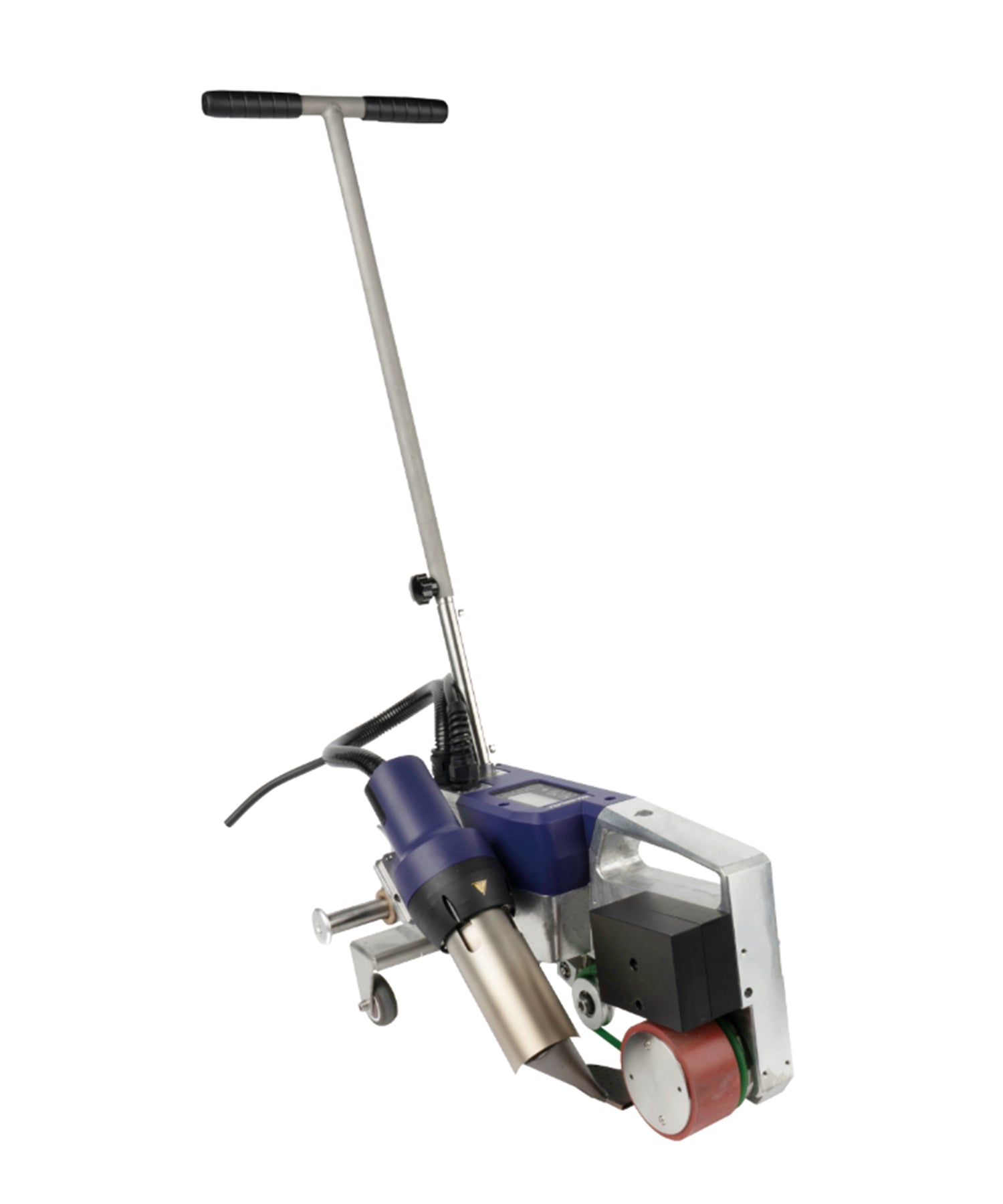
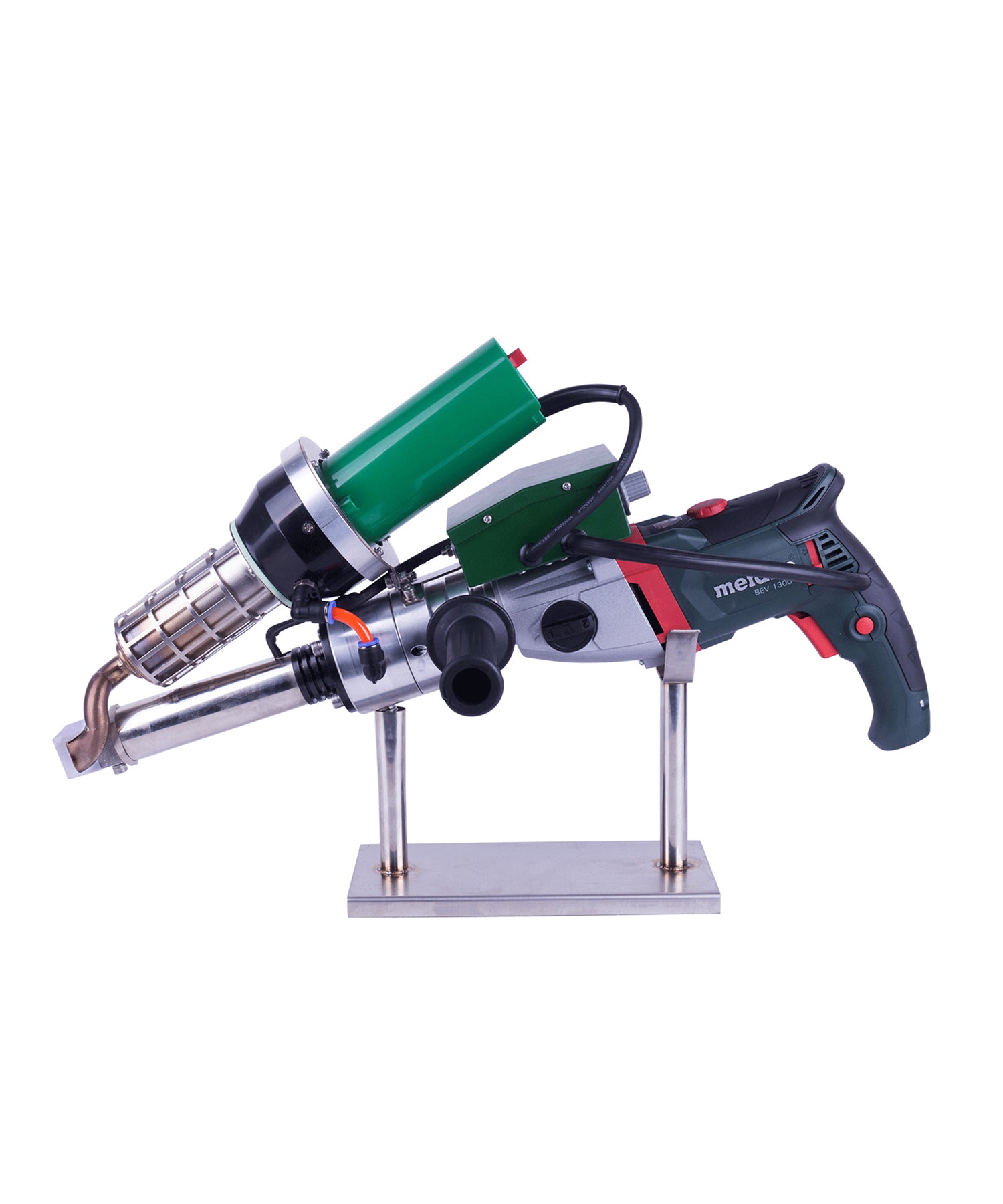
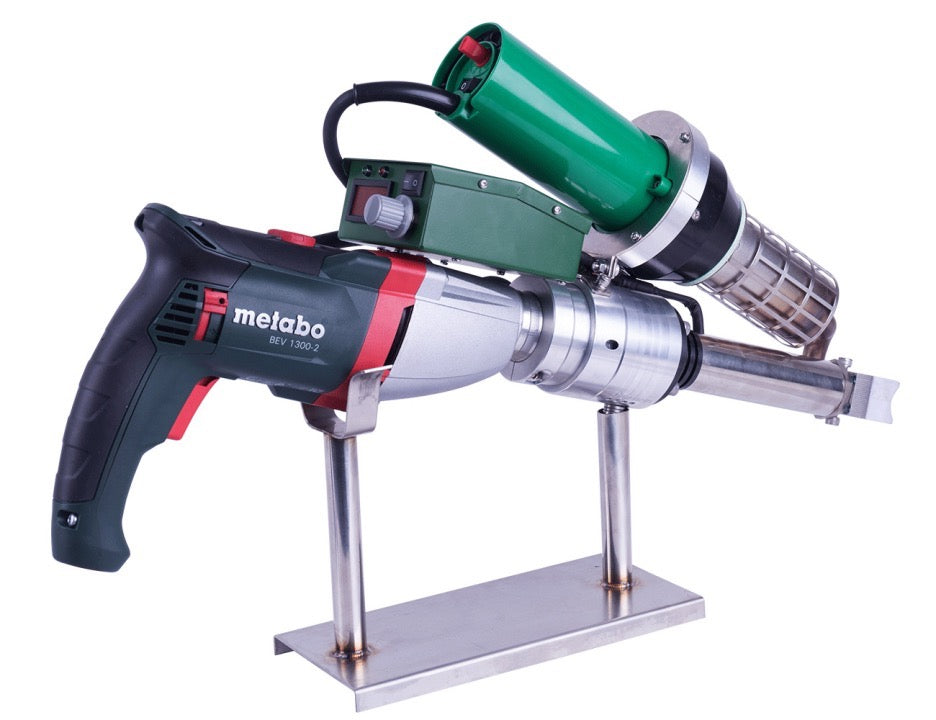
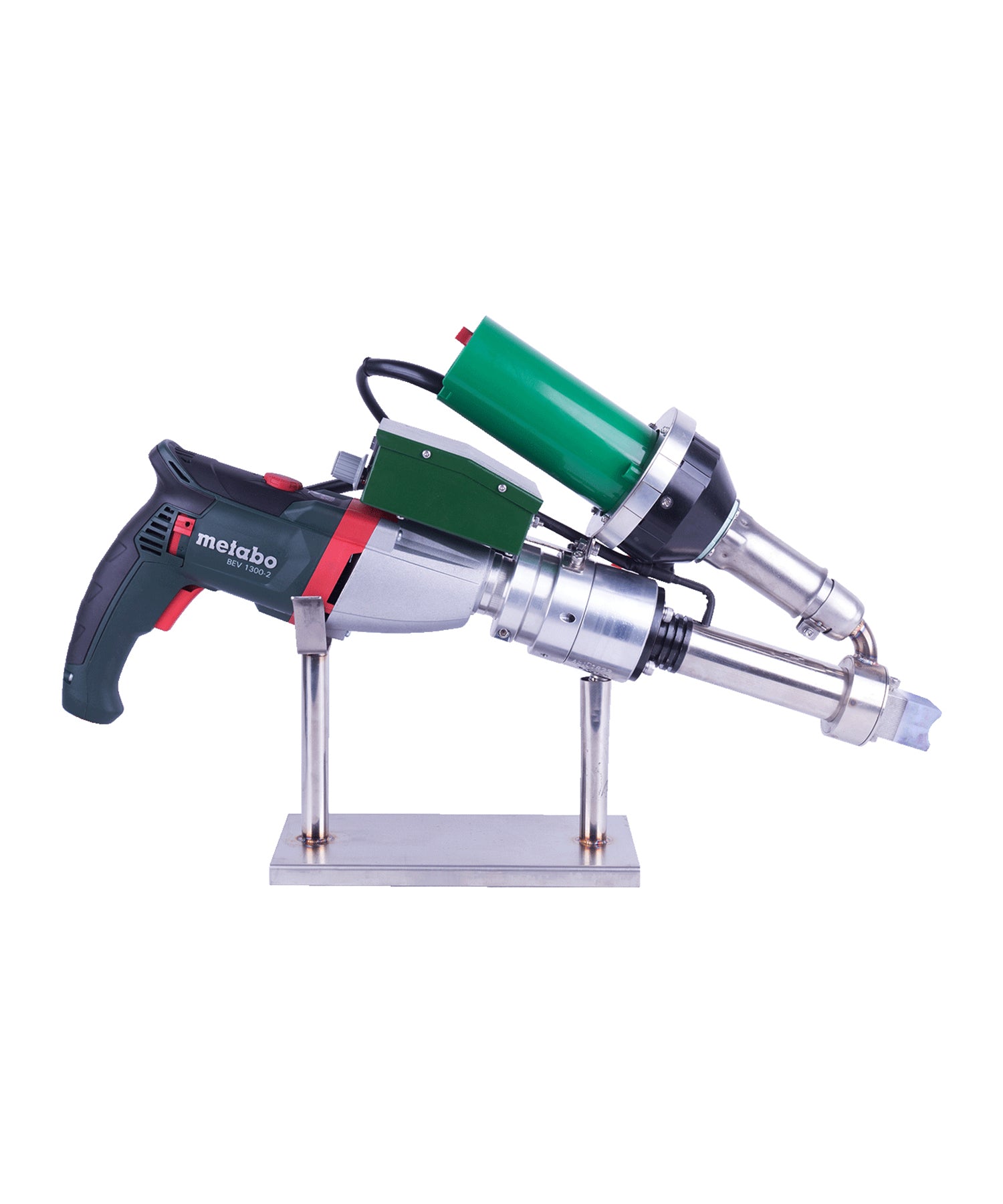
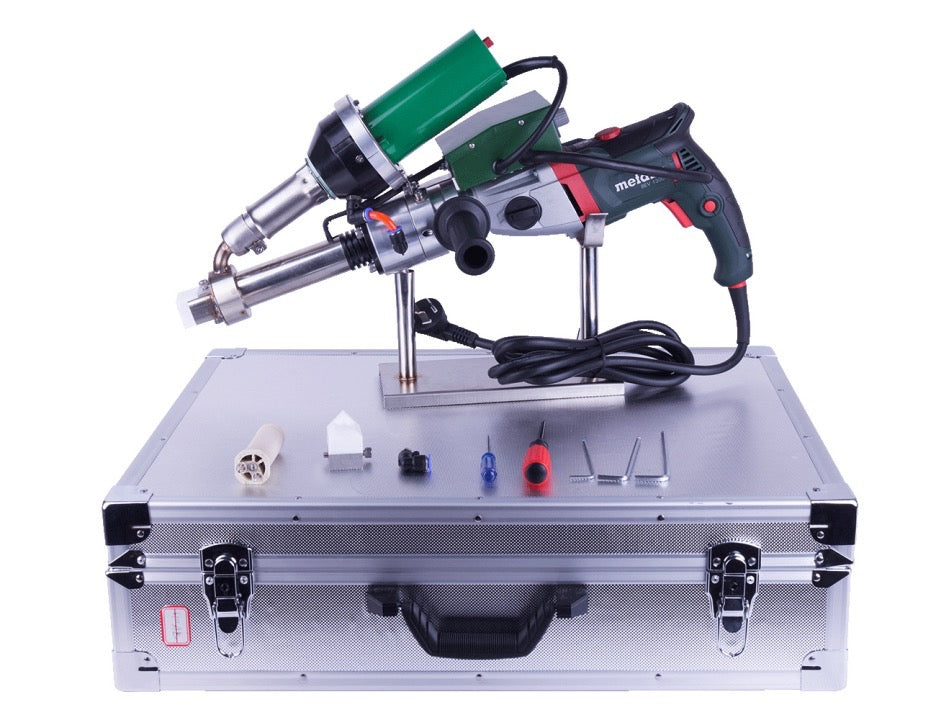
Automatic Roof Welding Machine Systems

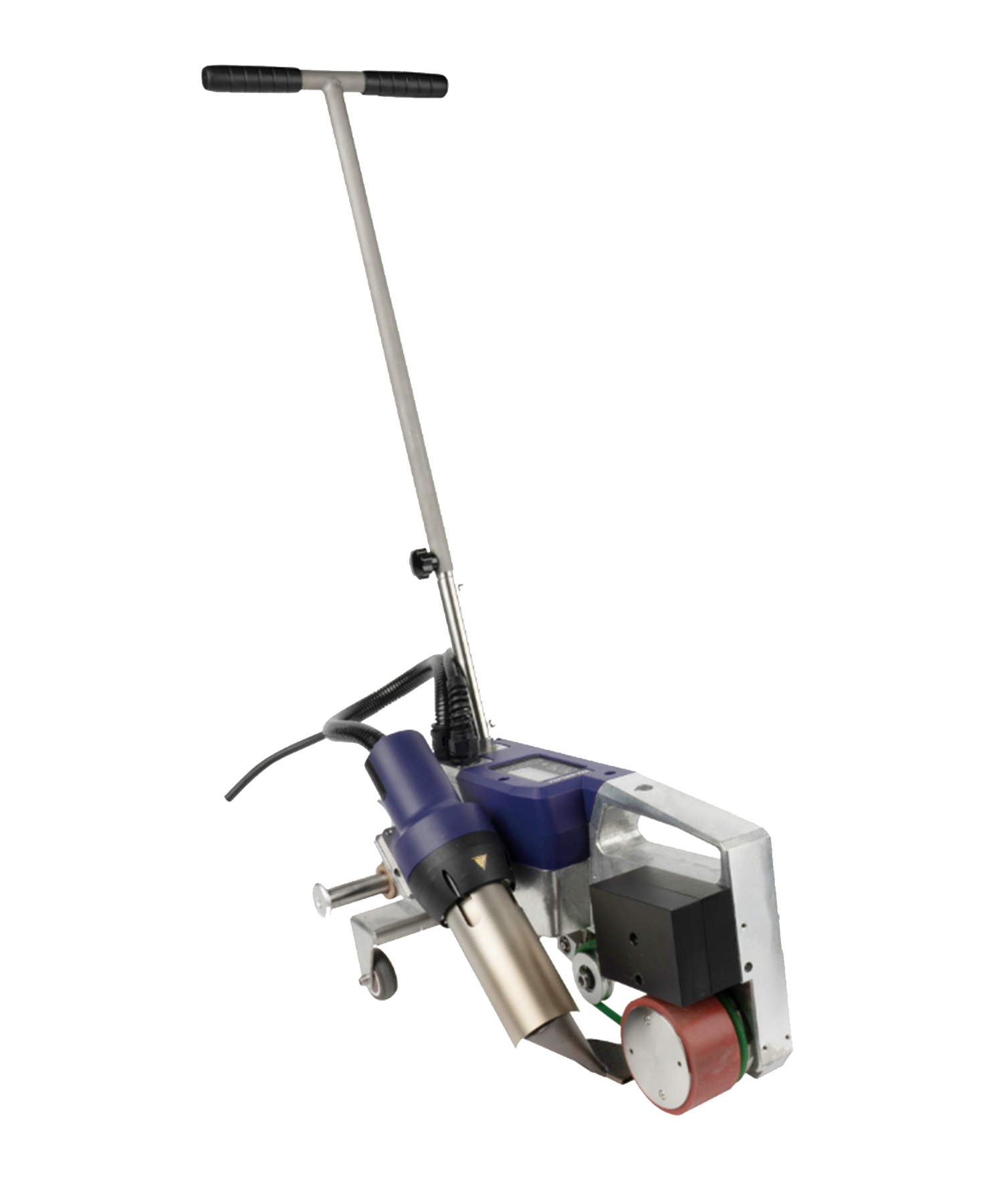
Automatic roof welders are core equipment for large-scale roofing projects, mainly consisting of the following components:
Main Unit: Equipped with digital temperature control systems for precise welding temperature adjustment (typically 150-450°C)
Travel Mechanism: Features variable frequency drive with adjustable speed (0.5-5 meters/minute)
Hot Air System: Delivers airflow up to 200-500L/min
Technical Advantages:
Increases welding efficiency by 3-5 times compared to manual operation
Achieves seam strength exceeding 90% of base material
Maintains weld uniformity within ±2mm tolerance
Typical Applications:
Welding TPO/PVC waterproof membranes for large factory buildings
Continuous welding for airport terminal roofs
Installation of photovoltaic roof integration systems
Operational Notes:
① Conduct test welds (≥300mm length) before formal work
② Preheat substrate when ambient temperature is below 5°C
③ Match travel speed to material thickness (recommend 2m/min for 1.5mm membranes)
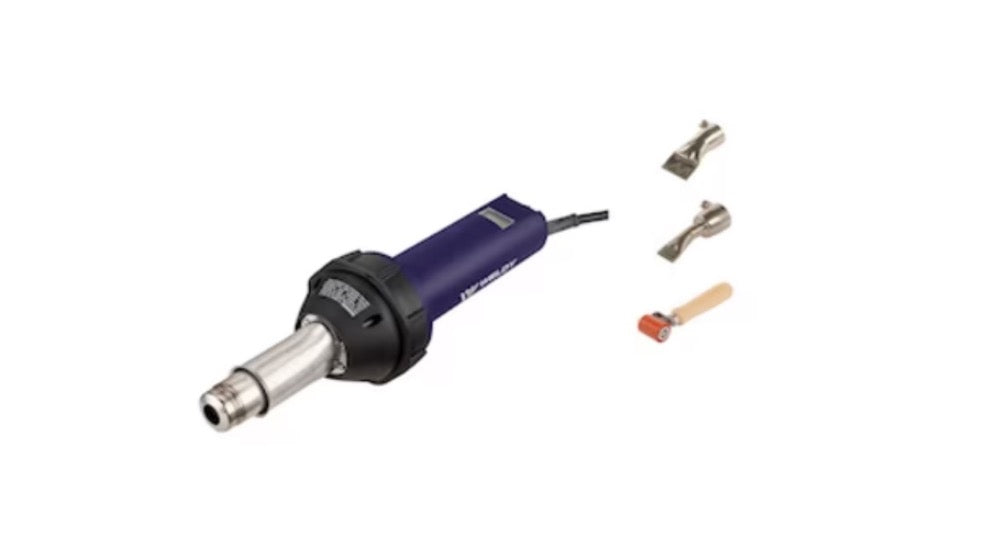
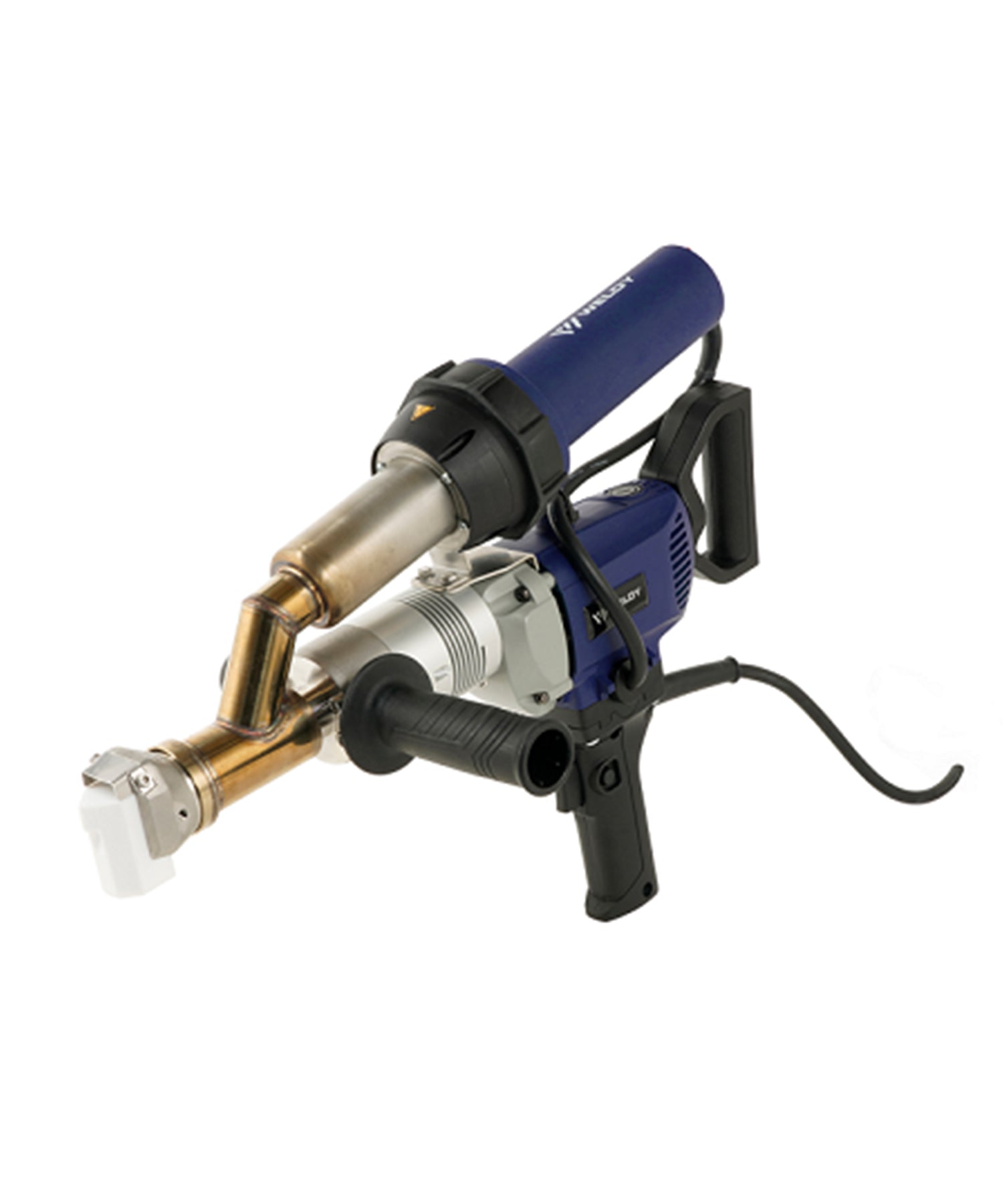
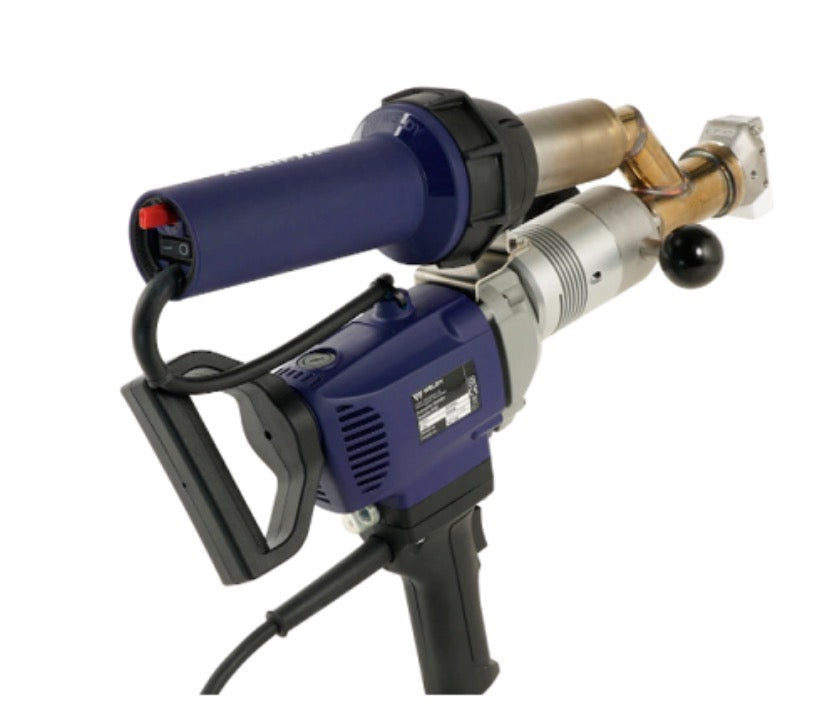
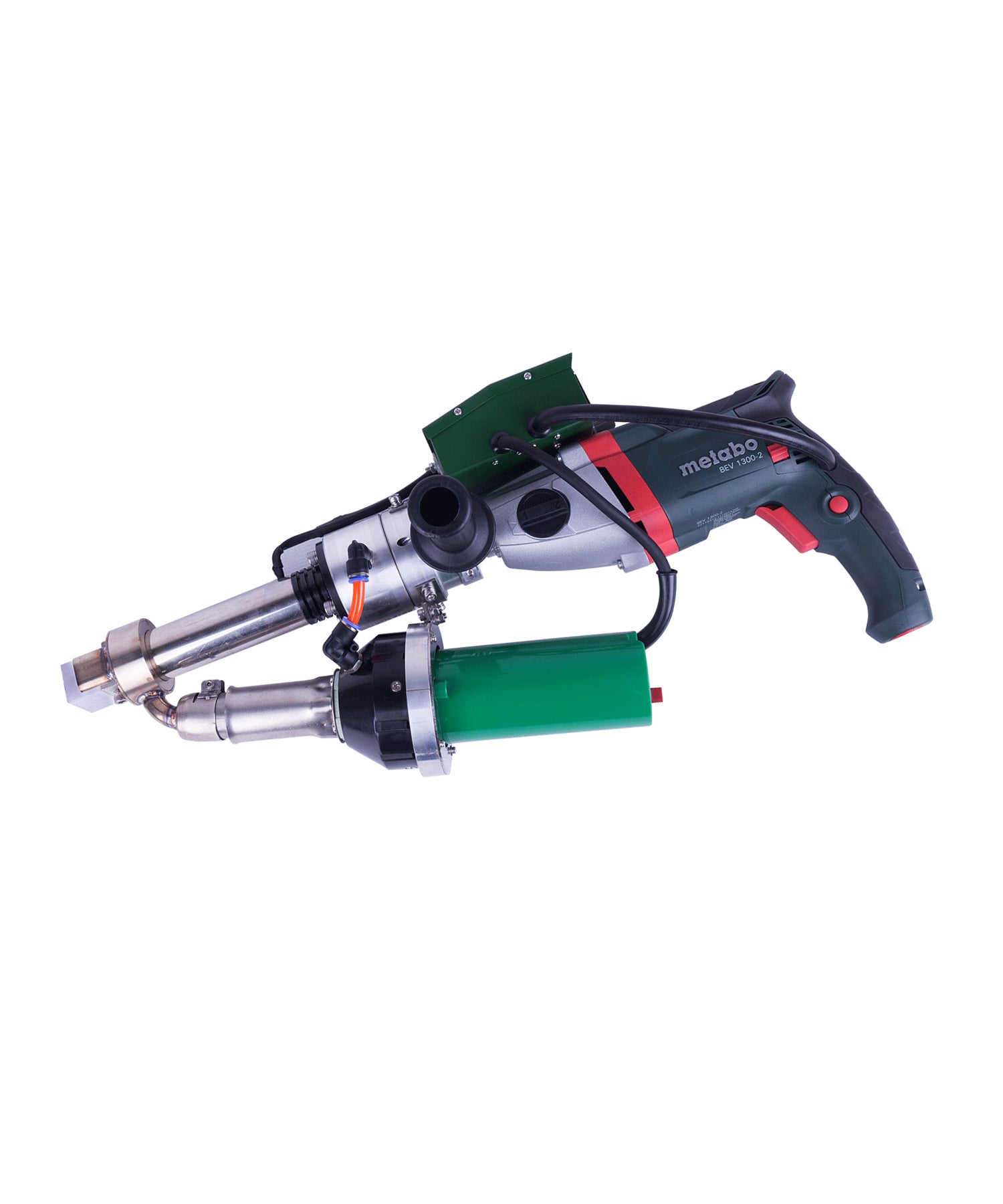
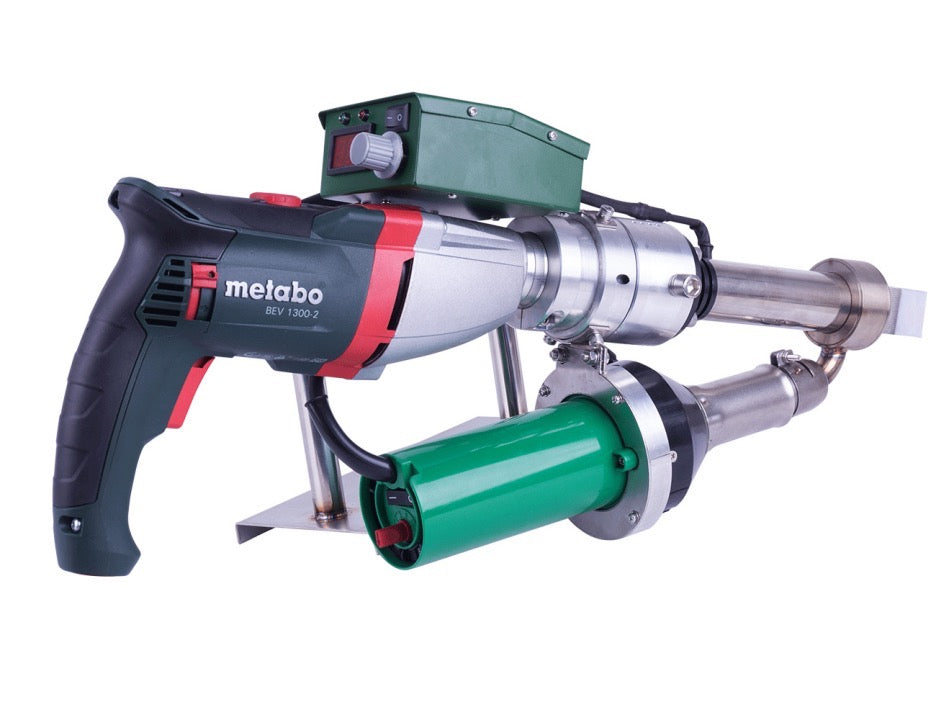
Manual Hot Air Welding Tools
Essential for detail work and repairs:
Hot Air Guns:
Power: 2000-3000W
Temperature range: Adjustable 50-600°C
Includes various nozzles (round/flat, etc.)
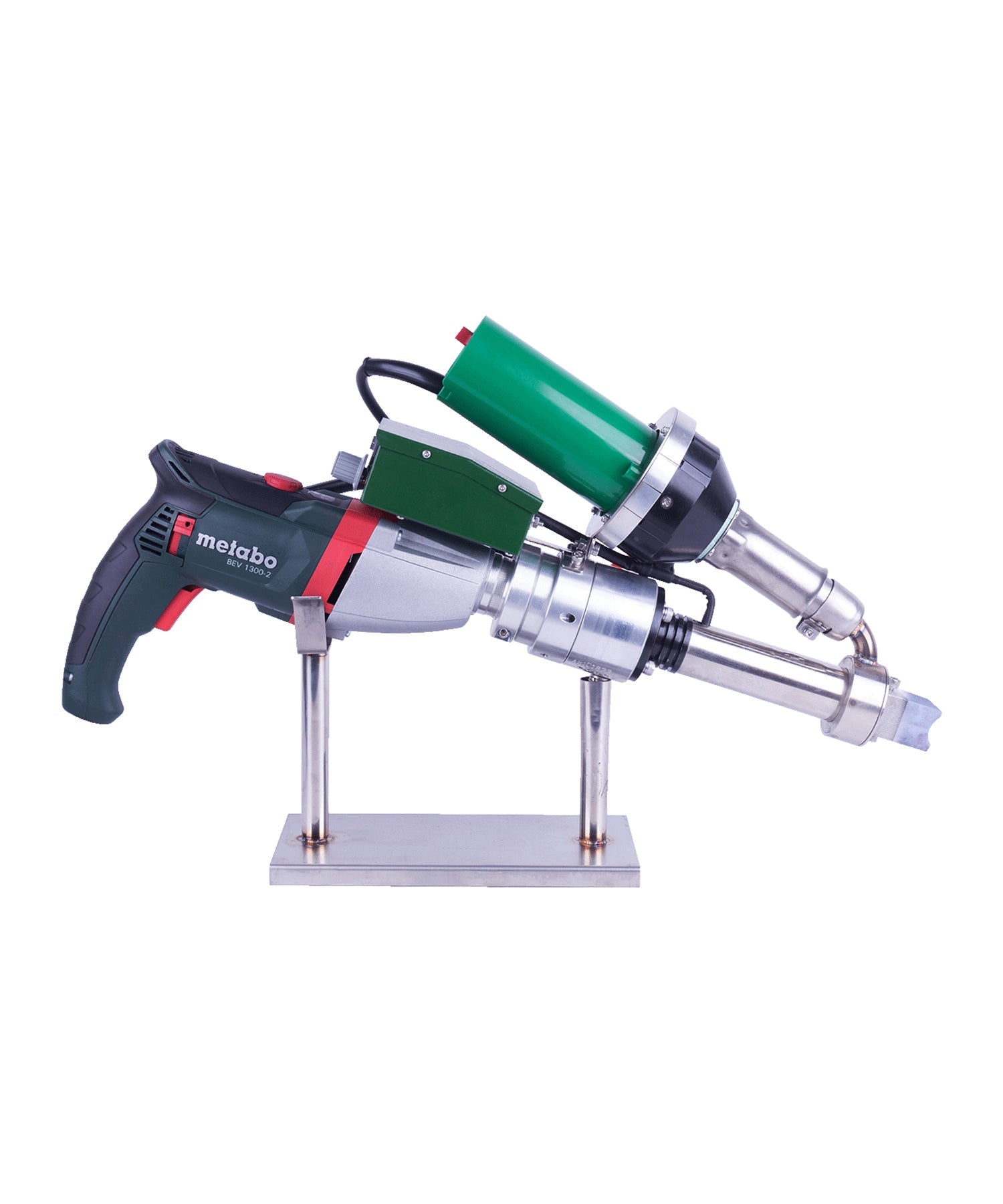
Extrusion Guns:
Suitable for materials >3mm thick
Welding rod diameter: 3-5mm
Feed speed: 0.5-3m/min
Application Scenarios:
Complex joints like pipe penetrations and gutters
Reinforcement of inside/outside corners
Localized damage repairs
Techniques:
Maintain 45° angle between gun and work surface
Control welding pressure at 0.2-0.3MPa
Ensure ≥50mm overlap width
Pressure Roller Systems
Critical auxiliary tools for weld quality:
Silicone Pressure Wheels:
Hardness: 60-80 Shore A
Operating temperature: -20°C to 150°C
Sizes: φ50-100mm
Heated Rollers with Temperature Control:
Surface temperature: 80-120°C
Adjustable pressure: 5-20kg
Key Points:
① Roll immediately after welding (<10 second interval)
② Follow "advance then press" sequence
③ Use shaped rollers (e.g., L-type) for complex areas
Power System Solutions
Tailored configurations for different environments:
Diesel Generators:
Power: 10-50kVA
Recommended brands: Yamaha/Honda
Suitable for sites without grid power
Lithium Battery Systems:
Voltage: 48V/72V
Runtime: 4-8 hours
Ideal for indoor renovation projects
Power Allocation Principles:
Dedicated circuit for automatic welders (≥32A)
Calculate peak load for multiple devices
Recommend 20% power reserve
Supporting Inspection Equipment
Complete welding systems should include:
Weld Inspection Devices:
Vacuum testing (negative pressure ≥0.03MPa)
Spark testing (15-30kV voltage)
Infrared Thermal Cameras:
Temperature resolution: 0.1°C
Detects defects like cold welds/overheating
Acceptance Standards:
Peel strength ≥50N/cm (EN 12316-1)
Air-tightness maintained for 30 minutes
Equipment Maintenance
Key measures to prolong service life:
Routine Care:
Clean welder filters weekly
Lubricate rails monthly
Quarterly cable insulation checks
Storage Conditions:
Humidity <60%
Drain water lines in winter
Disconnect batteries for long-term storage
Safety Gear
Essential PPE includes:
Heat-resistant gloves (withstands 500°C)
Respirators (organic vapor cartridges)
Anti-static workwear
Safety goggles (with side shields)
Conclusion
A complete roof welding system requires an investment of approximately ¥150,000-500,000. For enterprises with annual construction volumes exceeding 50,000m², we recommend configuring 2 automatic welders plus 10 manual tool sets. Proper use and maintenance of welding equipment can not only improve efficiency but also ensure roof systems meet 20+ year design lifespans. When purchasing, prioritize manufacturers with EN 13067 certification.





















Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.